PID Controller Simulator
Adjust the **PID gains** below and observe how the system responds in real-time.
📖 Understanding PID Gains
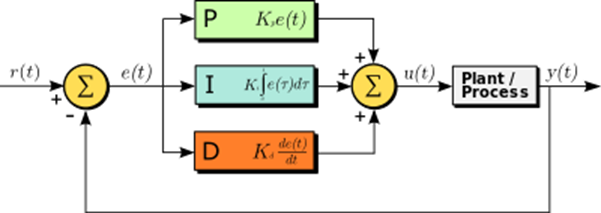
A **PID Controller** continuously adjusts a system to maintain a desired output by calculating an error value and applying corrections. These corrections are determined by **three gains**:
- P (Proportional Gain - Kp): Reacts to the current error. A higher Kp makes the system respond more aggressively.
- I (Integral Gain - Ki): Accounts for past errors. This eliminates steady-state error but can cause overshoot if too high.
- D (Derivative Gain - Kd): Predicts future errors based on the rate of change. Helps smooth out the system response.
By adjusting **Kp, Ki, and Kd**, you can **fine-tune the system’s response** to be stable, fast, and accurate.
Learn more about PID controllers🖥️ PID Block Diagram